what is a "drunken forest" and what does it have to do with the topography of eastern europe?
 Several of the oldest cities of Northwestern Europe are highlighted in this astronaut'due south photo from 00:25 GMT on 10 Baronial 2011  | |
| Area | x,180,000 km2 (3,930,000 sq mi)[north] (6th) |
|---|---|
| Population | 742,452,000[n] (2013; tertiary) |
| Population density | 72.9/kmtwo (188/sq mi) (2nd) |
| Demonym | European |
| Countries | 50 sovereign states v with limited recognition |
| Dependencies | 4 dependencies |
| Languages | ~225 languages[1] |
| Time zones | UTC−1 to UTC+5 |
Europe is traditionally defined as one of seven continents. Physiographically, information technology is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known equally Eurasia (or the larger Afro-Eurasia); Asia occupies the eastern bulk of this continuous landmass and all share a mutual continental shelf. Europe's eastern borderland is delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia, which is the largest country by land area in the continent. The southeast boundary with Asia is non universally defined, only the modernistic definition is generally the Ural River or, less unremarkably, the Emba River. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains (or, less normally, the river Kura in the Caucasus), and on to the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean. Iceland, though on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and nearer to Greenland (Northward America) than Mainland Europe, is generally included in Europe for cultural reasons and because it is over twice as close to mainland Europe as mainland Northward America. There is ongoing debate on where the geographical centre of Europe falls.
This video was taken by the crew of Expedition 30 on board the ISS on a pass over Europe. The ii videos were shot simultaneously using different cameras: 1 pointing toward the northeast, and ane pointing toward the eastward.
Overview [edit]

Satellite image of Europe past dark
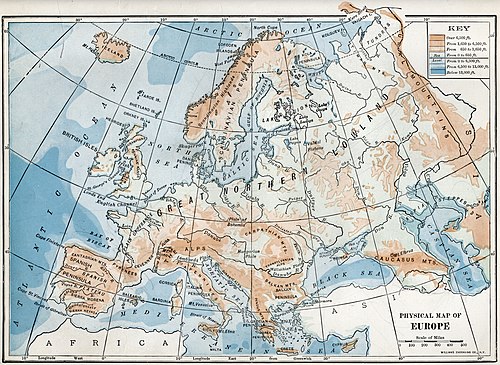
1916 physical map of Europe

Some geographical texts refer to a Eurasian continent given that Europe is not surrounded by sea and its southeastern border has always been variously defined for centuries.
In terms of shape, Europe is a collection of continued peninsulas and nearby islands. The ii largest peninsulas are mainland Europe and Scandinavia to the due north, divided from each other past the Baltic Sea. 3 smaller peninsulas—Iberia, Italia, and the Balkans—emerge from the southern margin of the mainland. The Balkan peninsula is separated from Asia by the Black and Aegean Seas. Italia is separated from the Balkans by the Adriatic Sea, and from Iberia by the Mediterranean Sea, which besides separates Europe from Africa. E, mainland Europe widens much like the oral fissure of a funnel, until the boundary with Asia is reached at the Ural Mountains and Ural River, the Caspian Sea, and the Caucasus Mountains.
Land relief in Europe shows great variation within relatively small-scale areas. The southern regions are mountainous while moving north the terrain descends from the high Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians, through hilly uplands, into broad, low northern plains, which are vast in the eastward. An arc of uplands also exists along the northwestern seaboard, beginning in southwestern Ireland, continuing beyond through western and northern United kingdom, and up along the mountainous, fjord-cut spine of Kingdom of norway.
This description is simplified. Sub-regions such equally Iberia and Italy contain their ain complex features, as does mainland Europe itself, where the relief contains many plateaus, river valleys, and basins that complicate the general trend. Iceland and the British Isles are special cases. The former is of North Atlantic volcanic formation, while the latter consist of upland areas once joined to the mainland until cut off by ascent sea levels.
Peninsula of peninsulas [edit]
Europe is sometimes called a "peninsula of peninsulas", to draw attention to the fact that Europe is a relatively minor, elongated bagginess to Asia, and that a large function of Europe is made up of peninsulas.[two] A prehistoric perspective would include United kingdom and Ireland as the core of a further very meaning European peninsula prior to the post-glacial rising in sea-levels.[three]
Partial list of European peninsulas
- Absheron peninsula
- Balkan peninsula
- Peloponnese
- Chalkidiki
- Istria
- Gallipoli
- Brittany
- Cotentin Peninsula
- Crimea
- Fennoscandian Peninsula
- Kola Peninsula
- Scandinavian Peninsula
- Iberian Peninsula
- Italian Peninsula
- Jutland
- Kanin Peninsula
Geology [edit]

The coast of Europe is heavily indented with bays and gulfs, as here in Hellenic republic.
Europe'due south about significant geological feature is the dichotomy between the highlands and mountains of Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern manifestly ranging from Great Great britain in the due west to the Ural Mountains in the e.[ citation needed ] These two halves are separated past the mountain chains of the Pyrenees and the Alps/Carpathians. The northern plains are delimited in the west by the Scandinavian mountains and the mountainous parts of the British Isles. The major shallow water bodies submerging parts of the northern plains are the Celtic Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Ocean complex, and the Barents Sea.
The northern manifestly contains the old geological continent of Baltica, so may be regarded equally the "main continent", while peripheral highlands and mountainous regions in south and w establish fragments from various other geological continents.
The geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex, and gives ascent to the wide multifariousness of landscapes found beyond the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary.
| | This section needs expansion. Yous can help by adding to it. (March 2011) |
Population [edit]
Figures for the population of Europe vary according to which definition of European boundaries is used. The population inside the standard physical geographical boundaries was 701 million in 2005 according to the United nations. In 2000 the population was 857 million, using a definition which includes the whole of the transcontinental countries of Russian federation and Turkey. Population growth is insufficiently slow, and median age insufficiently loftier in relation to the world'south other continents.
Rivers [edit]

The most important rivers in Europe are Danube, Volga, Rhine, Elbe, Oder and Dnieper, amidst others.[ further explanation needed ]
European rivers by length [edit]
The longest rivers in Europe, direct flowing into the World Ocean or Endorheic basins, with their approximate lengths:[4] [5]
- Volga - 3,690 km (2,290 mi)
- Danube - 2,860 km (i,780 mi)
- Ural - two,428 km (1,509 mi)
- Dnieper - 2,290 km (1,420 mi)
- Don - ane,950 km (one,210 mi)
- Pechora - ane,809 km (1,124 mi)
- Kama - i,805 km (1,122 mi)
- Oka - one,500 km (930 mi)
- Dniester - 1,352 km (840 mi)
- Rhine - one,236 km (768 mi)
- Elbe - ane,091 km (678 mi)
- Vistula - ane,047 km (651 mi)
- Tagus - 1,038 km (645 mi)
- Daugava - 1,020 km (630 mi)
- Loire - 1,012 km (629 mi)
- Ebro - 960 km (600 mi)
- Prut - 953 km (592 mi)
- Neman - 937 km (582 mi)
- Meuse - 925 km (575 mi)
- Douro - 897 km (557 mi)
- Kuban River - 870 km (540 mi)
- Mezen - 857 km (533 mi)[six]
- Oder - 854 km (531 mi)
- Guadiana - 829 km (515 mi)
- Rhône - 815 km (506 mi)
- Kuma - 802 km (498 mi)
- Seine - 776 km (482 mi)
- Mureș - 761 km (473 mi)
- Northern Dvina - 744 km (462 mi)
- Po - 682 km (424 mi)
- Guadalquivir - 657 km (408 mi)
- Bolshoy Uzen - 650 km (400 mi)
- Siret - 647 km (402 mi)
- Terek - 623 km (387 mi)
- Glomma - 604 km (375 mi) (Kingdom of norway'due south longest and most voluminous river)
- Garonne - 602 km (374 mi)
- Kemijoki - 550 km (340 mi)
- Chief 525 km (326 mi) (longest (correct) tributary of Rhine)
- Torne - 522 km (324 mi)
- Dalälven - 520 km (320 mi)
- Maritsa - 515 km (320 mi)
- Marne - 514 km (319 mi) (major tributary of the Seine)
- Neris - 510 km (320 mi)
- Júcar - 509 km (316 mi)
- Dordogne - 483 km (300 mi)
- Ume - 470 km (290 mi)
- Ångerman - 460 km (290 mi) (Sweden's longest rivers)
- Lule - 460 km (290 mi)
- Gauja - 452 km (281 mi)
- Weser - 452 km (281 mi)
- Kalix - 450 km (280 mi)
European rivers by discharge [edit]
The 15 rivers of Europe by boilerplate discharge, including only rivers directly flowing into the World Ocean or Endorheic basins:
- Volga - eight,087 thou³/s (largest river in Eastern Europe)
- Danube - 6,450 m³/south (largest river in Central Europe)
- Pechora - iv,380m³/s
- Northern Dvina - iii,330m³/southward
- Neva - 2,490 chiliad³/southward
- Rhine - two,315 m³/southward) (largest river in Western Europe)
- Rhône - 1,900 m³/s (largest river in France)
- Dnieper - one,700 m³/s
- Po - ane,460 m³/south (largest river in Italian republic)
- Vistula - 1,080 grand³/s (largest river in Poland)
- Don - 890 grand³/s
- Mezen - 890 thou³/due south
- Loire - 889 chiliad³/s (longest river in French republic)
- Elbe - 860 one thousand³/s
- Glomma - 709 m³/s (Norway's longest and most voluminous river)
Lakes and inland seas [edit]
Major islands [edit]
Aegean Islands, Åland, Balearic Islands, Corsica, Crete, Republic of cyprus (Adjacent to Asia), Fyn, Faroe Islands, Gotland, Keen Britain, Hinnøya, Iceland, Ionian Islands, Ireland, Malta, North Jutlandic Island, Saaremaa, Sardinia, Senja, Sicily, Svalbard and Zealand.
Plains and lowlands [edit]

View across the Bulgarian department of the Lower Danubian Plain towards the central Balkan Mountains 90 km away
- Cracking European Evidently, the largest landscape feature of Europe
- East European Plain
- Lower Danubian Plain, between Balkan Mountains and Southern Carpathians
- Danubian Plain (Bulgaria)
- Wallachian Obviously
- Lower Danubian Plain, between Balkan Mountains and Southern Carpathians
- North European Plain
- North German Obviously (German section)
- Beauce, France
- East European Plain
- Baetic Low (Andalusian Evidently), between Sierra Morena and Baetic Organisation
- British Lowlands
- Central Swedish lowland
- Ebro Basin (Ebro Depression), between Pyrenees and Sistema Ibérico
- Meseta Central is a loftier manifestly plateau in key Spain (occupies roughly 40% of the state), betwixt Cantabrian Mountains and Sistema Central
- Pannonian Plain, between Alps, Dinaric Mountains and Carpathian Mountains
- Po Valley, also known equally Padan Obviously, between Alps and Apennines
- Swiss Central Plateau, between the Jura Mountains and Swiss Alps
- Upper Rhine Plain, betwixt Vosges Mountains and Black Wood Mountains
- Upper Thracian Plain, betwixt Balkan Mountains (Sredna Gora) and Rila-Rhodope massif
- Other European coastal plains
Mountain ranges [edit]

Some of Europe's major mount ranges are:
- Alps, in Central Western Europe
- Western Alps
- Eastern Alps
- Southern Alps
- Northern Alps
- Apennines, which run through Italian republic
- Baetic System, Espana, Iberian Peninsula

Musala, highest summit of the Balkans seen from Yastrebets. The chalet Musala and the Everest shelter can be seen as well.
- Balkan Mountains, mainly Bulgaria, central Balkan Peninsula
- Sredna Gora Mountain range in central Bulgaria, situated s of and parallel to the Balkan Mountains
- Maverick and other Variscan massifs (pre-Alpine mount ranges) - Jura Mountains, Vosges, Palatinate Forest, Black Forest, Ore Mountains, Sudetes
- Cantabrian Mountains, which run beyond northern Kingdom of spain
- Carpathian Mountains, a major mount range in Cardinal and Southern Europe
- Southern Carpathians, Romania
- Tatra Mountains, Slovakia and Poland
- Caucasus Mountains, which also dissever Europe and Asia
- Crimean Mountains

- Dinaric Alps, a mount range in the Balkans
- Pindus Mountains, Albania and Greece
- Pyrenees, the natural border betwixt France and Spain
- Rila-Rhodope mountain arrangement composed by massifs, including Pirin Mount and Osogovo-Belasitsa mountain concatenation, mainly Bulgaria
- Šar-Korab-Jakupica-Baba-Kajmakčalan-Olympus, Albania, Northern Macedonia and Greece[seven]
- Scandinavian Mountains, a mountain range which runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula, includes the Kjølen mountains
- Scottish Highlands (including the Cairngorms) in the Britain.
- Sierra Morena, Spain
- Sistema Ibérico, Espana
- Sistema Primal, Spain
- Ural Mountains, which course the boundary between Europe and Asia
Country area in unlike classes of European mountainous terrain (nomenclature from UNEP-WCMC):

| Distance | Area (km2) | % Area |
|---|---|---|
| ≥4500m | 1 | 0.00% |
| 3500-4500m | 225 | 0.00% |
| 2500-3500m | 497,886 | 4.89% |
| 1500-2500m & gradient ≥2° | 145,838 | 1.43% |
| 1000-1500m & slope ≥5° or local height range >300m | 345,255 | three.39% |
| 300-1000m and local elevation range >300m | 1,222,104 | 12.00% |
| Mountainous Full | 2,211,308 | 21.72% |
| Europe TOTAL | x,180,000 | 100.00% |
Temperature and precipitation [edit]

The loftier mountainous areas of Europe are colder and take higher precipitation than lower areas, as is truthful of mountainous areas in general. Europe has less precipitation in the east than in central and western Europe. The temperature difference between summertime and winter gradually increases from coastal northwest Europe to southeast inland Europe, ranging from Ireland, with a temperature difference of but 10 °C from the warmest to the coldest month, to the area north of the Caspian Bounding main, with a temperature difference of twoscore °C. January average range from 13 °C in southern Spain and southern Greek islands to -20 °C in the northeastern function of European Russia. Desert climates are found in the European portion of Republic of kazakhstan and South Eastern Spain.
Western Europe and parts of Cardinal Europe more often than not fall into the temperate maritime climate (Cfb), the southern office is more often than not a Mediterranean climate (mostly Csa, smaller area with Csb), the north-central part and east into central Russia is more often than not a humid continental climate (Dfb) and the northern part of the continent is a subarctic climate (Dfc). In the farthermost northern part (northernmost Russia; Svalbard), bordering the Arctic Ocean, is tundra climate (Et). Mountain ranges, such as the Alps and the Carpathian mountains, take a highland climate with big variations according to altitude and latitude.
Climate [edit]

Landlocked countries [edit]
The landlocked countries in Europe are: Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Belarus, Czech Commonwealth, Republic of hungary, Kosovo, Liechtenstein (which is doubly landlocked), Grand duchy of luxembourg, North Macedonia, Moldova, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, Switzerland, The holy see
Switzerland, Principality of liechtenstein, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Serbia, and Northward Macedonia constitute a contiguous landlocked agglomeration of eight countries in Central Europe and the Balkans, stretching from Geneva all the mode to Skopje. The other landlocked countries are "standalone" landlocked, not bordering any other such European ane (the emphasis is necessary, since Republic of kazakhstan borders Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan, thus forming a vast landlocked expanse in Primal Asia).
Countries consisting solely of islands or parts of islands [edit]
- Cyprus
- Republic of iceland
- Republic of ireland
- Malta
- United Kingdom
Countries bordering or spanning another continent [edit]
| Eurasia | Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russian federation, Turkey, Greece (some Aegean islands and Kastelorizo isle in southeastern Mediterranean) |
| Europe-Africa | Malta, Espana (Ceuta, Melilla and Canary Islands), Italian republic (Lampedusa and Lampione), Portugal (Madeira),[eight] France (Réunion and Mayotte) |
| Europe-South America | French republic (French Guiana) |
| Europe-North America | France (Guadeloupe, Martinique, and St. Pierre et Miquelon), Iceland, Kingdom of denmark (Greenland), Netherlands (Bonaire, Saba, and St. Eustatius), Portugal (Corvo Island, Flores Island) |
[edit]
- Andorra
- Grand duchy of luxembourg
- Monaco
- San Marino
- Vatican Metropolis
Countries whose upper-case letter is not the well-nigh populous [edit]
| Land | Majuscule | Largest city or municipality |
|---|---|---|
| | Vaduz | Schaan |
| | Valletta | Birkirkara |
| | City of San Marino | Serravalle |
| | Bern | Zurich |
| | Ankara | Istanbul |
Note: Italy'southward capital, Rome, is the country'southward largest city if but the municipality (comune) is considered. Greater Milan is the largest Metropolitan Expanse in Italy.
Brussels is considered to be the largest urban center of Kingdom of belgium, according to the population of the Brussels-Capital Region. The population of the City of Brussels is ~175,000. Antwerp is the biggest urban center of the land.
List of countries by the number of other countries they border [edit]

Map of European countries past number of neighbouring countries.
| 14 | Russian federation (Including Kaliningrad) |
| 11 | French republic (Including overseas departments and territories) |
| 9 | Germany |
| 8 | Republic of austria, Serbia, Turkey |
| 7 | Hungary, Poland, Ukraine |
| half dozen | Italy |
| 5 | Azerbaijan, Republic of belarus, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kazakhstan, Romania, North Macedonia, Slovakia, Espana (Including Ceuta and Melilla), Switzerland |
| iv | Republic of albania, Armenia, Belgium, the Czech republic, Georgia, Greece, Kosovo, Latvia, Republic of lithuania, Montenegro, Slovenia |
| 3 | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Finland, Netherlands (Including Sint Maarten), Norway, Grand duchy of luxembourg |
| 2 | Andorra, Estonia, Liechtenstein, Moldova, Sweden |
| i | Kingdom of denmark, Ireland, Monaco, Portugal, San Marino, United Kingdom, The holy see |
| 0 | Iceland, Cyprus, Malta |
See too [edit]
- Regions of Europe
- European grid
- European Marriage
- Western Europe
- Central Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Northern Europe
- Southern Europe
- Southeast Europe
- Extreme points of Europe
- Intermediate Region
- Extreme points of the European Wedlock
- List of European ultra-prominent peaks
- Listing of the highest European ultra-prominent peaks
- List of mountain ranges
- Southernmost glacial mass in Europe
- Countries adjoining the European Union
- Extreme points of Eurasia
- Extreme points of Afro-Eurasia
- Geography of the European Union
- Special member country territories and the Eu
- Age of Discovery
- Explorers of Russia
Notes [edit]
- ^ Language facts – European 24-hour interval of languages, Quango of Europe. Retrieved xxx July 2015.
- ^ Europe: Concrete Geography National Geographic - Education
- ^ "The moment Uk became an isle". BBC News magazine. BBC. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ "European Rivers". worldatlas.com.
- ^ "River Systems of the World". Archived from the original on 2009-09-19.
- ^ Мезень (река). Great Soviet Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on August 10, 2011.
- ^ Greek-Albanian Ranges peakbagger.com
- ^ Peoples of Africa. Marshall Cavendish. 2000. ISBN9780761471585.
External links [edit]
-
 Media related to Geography of Europe at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Geography of Europe at Wikimedia Commons
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Europe
0 Response to "what is a "drunken forest" and what does it have to do with the topography of eastern europe?"
Post a Comment