How to Upload an Image Sitemap to Google
I have been hearing all sorts of misunderstandings about sitemaps. Again and again, every week. That'southward why I decided to create ane circuitous commodity with a printable cheat sheet. It will comprehend all of the best practices from the sitemap earth and disprove all of the misinterpretations well-nigh it.
I gathered all of the know-how and experience that I had accumulated by creating sitemaps for my work through the years.
And voila. Here is the article that will help yous to get the sitemap expert, whether you are a beginner or are already a professional.
In this commodity, you lot will find everything important:
- How sitemaps can help you with SEO
- Do you really need a sitemap? Observe it out
- Choose most suitable types of sitemaps for your website
- Brand your sitemaps in 4 steps:
- Create XML Sitemap & its extensions
- RSS feed & mRSS
- Create a structure with a Sitemap index
- Validate your sitemaps
- The last of import pace: Notify search engines about sitemaps

This article is really long. When yous need an answer to certain questions, bound to FAQ department:
- What is a sitemap for, are sitemaps important for SEO?
- How many types of sitemaps are there in SEO?
- How to find my sitemap URL?
- How to apply XML sitemap?
- How many sitemaps should I have?
- How to create a sitemap for Google?
- How to add together a sitemap to Google?
one. How sitemaps can help yous with SEO?
First, you should understand what a sitemap is, along with its main purpose.
What is the master purpose of sitemaps?
A Sitemap is a list of spider web pages created for web crawlers then they tin can detect your spider web content fast and easy. The search engine tin can apply a sitemap to see the newest pages on a website, or all the web pages together, including all images, video content, etc.
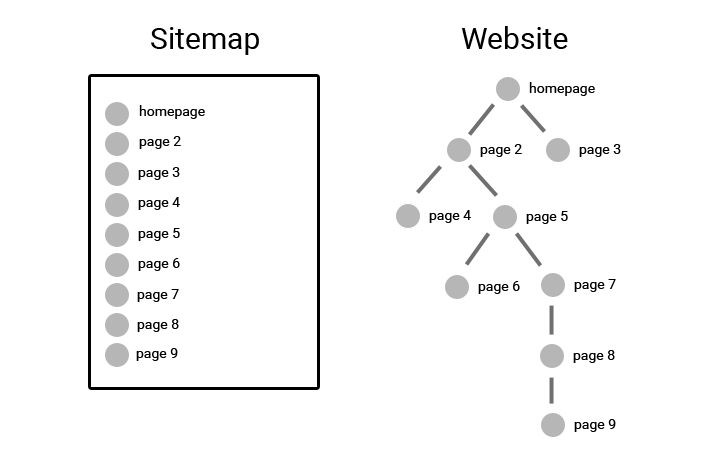
A search engine will find page ix in a sitemap immediately, within i visit of the file. On the website illustrated in a higher place, it will accept to bound through vi web pages to find folio 9.
SEO benefits of sitemaps
- Faster indexation: Search engine will discover out about new pages much faster, therefore, the indexation procedure and displaying the website in search results will be faster likewise. Sitemaps can assistance you with the deindexation too.
- Meliorate indexation of deep pages: Search engines tin can detect out the pages that were non discovered while crawling the website. But it doesn't necessarily hateful that all of them will be indexed.
- Monitoring of indexed pages: In combination with Google Search Panel, information technology is possible to detect out which URLs are covered in the sitemap that Google indexes.
Unfortunately, webmasters oftentimes give sitemaps credit, which they actually don't deserve. I take to say it articulate and loud:
Sitemaps don't help you lot with better search rankings.
A sitemap is non a ranking gene. Listing URLs into a sitemap has nothing influence on the higher search rankings.
URLs with a deep link level or lack of internal links get no or little link juice. With no link juice, search bots can notwithstanding consider these pages equally depression-quality, even if they are listed in sitemaps. Almost likely, the search engines will refuse to display them in SERPs anyway.
Did yous read the article up until this office? Great task. You know the main principles and the SEO benefits of sitemaps by now. Now, information technology will exist much easier to get a little deeper.
2. Do you need a sitemap?
A sitemap isn't necessary for every website. And if you need one, it doesn't exactly have to be a sitemap.xml. You can implement several types of sitemaps, like an RSS feed or special extensions for a sitemap.xml.

A sitemap is for you, if:
- Yous have a big website: A website with 100 pages isn't big. Fifty-fifty a website with 1,000 pages is still pretty pocket-sized, and a sitemap isn't actually necessary. For bigger sites, however, you should definitely consider information technology. Exercise you have 1 1000000 pages? Then you demand a sitemap.
- You have a new site: A sitemap helps crawlers to find a brand new website just afterward launch and to alphabetize the new pages much faster.
- You lot change your website'southward content frequently
- You demand to index your fresh content very fast: A sitemap helps to accelerate the indexation of newly added pages subsequently adding them to the sitemap, especially, when your site is in Google News.
You don't need a sitemap if your website is:
- One-page presentation
- A portfolio website
- Website of an organization
- Small-scale local business website
- SaaS awarding
Don't forget.
If a blog is part of your website, you should use an RSS feed for it.
3. What types of sitemaps are about suitable for your website?
Before you start to call back about how to code and implement sitemaps, y'all accept to choose the right type of sitemap to fit your needs. Here is the complete table:
| Type | Google/Bing compatibility | Purpose | Where to apply it |
|---|---|---|---|
| XML sitemap | Google, Bing | Better indexation of deep linked HTML pages | New or extensive website with circuitous navigation |
| Image XML sitemap | Google, Bing | Extension for images | Website with important epitome content |
| Video XML sitemap | Google, Bing | Extension for video | Website with video content |
| Mobile XML sitemap | Extension for mobile version pages | Website with a mobile version located on a divide URL without annotations in HTML | |
| Alternate language XML sitemap | Extension for pages in alternate languages | Website with more language mutations, but non providing the hreflang aspect in the HTML lawmaking or HTTP header | |
| Google News Sitemap | Rapid indexation of news | Website involved in Google News | |
| RSS feed / Atom | Google, Bing | Newest or updated HTML sites, images | Website with often added or updated content |
| mRSS | Google, Bing | RSS video extension | Website with often added or updated video content |
A sitemap can exist written every bit a simple text file. We don't deal more with it because it contains only a list of URLs. Other sitemap forms allow meliorate URL annotation.
Best practices for the sitemap types
Still not sure what sitemaps are nearly suitable for you?Here are my recommendations. Mouse over these website types:

This is a general recommendation about sitemap all-time practices for SEO. As that every website is unique. In one case you cull the type of sitemap, call up virtually its purposes.
Avoid static sitemap generators
Sitemap generator tools like XML-sitemaps.com are very pop. Y'all enter the URL of your website, and then the generator starts to crawl it and creates the sitemap. After that, you upload the generated sitemap file to the web server. It is easy to use, but information technology's likewise mostly useless and counterproductive. If you create new web pages, the sitemap remains the same. It volition not reflect the changes.
Why are XML sitemap generators useless?
1. Generated sitemaps volition exist outdated very apace
Equally I said in the start of this guide, ane of the principal benefits of a sitemap is that the search engine will discover out about the new pages much faster. The generator only gives you a snapshot of a website when the sitemap is generated, which is tough. It will be outdated very apace.
2. The unimportant URLs are listed
Every bit I wrote in the section "Which URLs should exist put in a sitemap", it'southward important to exclude not important URLs. Most sitemap generators put in all of the website URLs. Sure, you can delete all of the unnecessary URLs, simply you tin easily make a fault in the messy data.
3. Generator sees simply linked URLs
Y'all can add to sitemap URLs, which aren't linked from the website. Sitemap generator can't. Only don't forget, information technology doesn't necessarily hateful that all of the not-linked URLs will exist indexed.
And then, delight avoid using sitemap generators while you lot don't accept a very proficient reason to use them. What's a very good reason? For example, when your website is new, and you need to index information technology fast. In this instance, yous probably don't have the fourth dimension or the resources to create a dynamic sitemap, which would be updated regularly.
In most cases, you need a dynamic sitemap with regular updates. Let's see how to implement information technology.
4. How to make a sitemap
Now I am going to exist a piddling bit techy. All of the sitemaps described above are in XML format. There are two basic formats: XML sitemap and RSS.
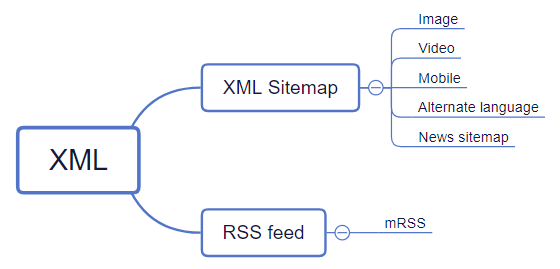
Sitemaps bureaucracy
With these formats, you will embrace everything. Each Bing & Google sitemap. So, you lot don't need to employ or know more about other formats, such as an Atom feed.
4.1. XML sitemap
i. Declaration
Crawlers recognize the sitemap by this declaration:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> <urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > </urlset> |
2. Calculation URLs
Tag <urlset> wraps URLs. Here is a uncomplicated sitemap with one URL:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-viii" ?> <urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > <url> <loc> http://world wide web.example.com/page1.html </loc> </url> </urlset> |
For adding more than URLs, y'all just put more <url> tags in in that location. Just one tag is required in a <url> tag and that is its location. Thanks to using <loc> tag, Google will know about all of the important URLs.
3. Adding lastmod to URLs
I as well strongly recommend wrapping an information about the terminal update of URL in the <url> tag. It tin can accelerate the recrawling of the URL with fresh content. You tin can exercise it with a <lastmod> tag like this:
| <url> <loc> http://world wide web.instance.com/page1.html </loc> <lastmod> 2017-10-20T17:xxx:00-02:00 </lastmod> </url> |
The consummate sitemap.xml instance:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-eight" ?> <urlset xmlns = "http://world wide web.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > <url> <loc> http://www.example.com/page1.html </loc> <lastmod> 2017-ten-20T17:xxx:00-02:00 </lastmod> </url> </urlset> |
Lastmod formatting
Lastmod uses a W3C date and time format. Allow's take a look at the value in the example above: Description of value 2017-x-20T17:30:00-02:00
| Part of the value | Description |
|---|---|
| 2017-10-20 | The engagement, 20th of October, 2017 |
| T | Separator between date and time |
| 17:30:00 | 17 hours, 30 minutes, 0 seconds |
| -02:00 | Time is observed in UTC time zone, and -02:00 means time is shifted 2 hours backwards. If you want to use the exact UTC, put a "Z" character instead (2017-10-20T17:30:00Z) |
You lot tin can add two more than tags into a sitemap, <changefreq> and <priority>. Google ignores them (Seroundtable.com, May 2015). John Mueller from Google confirmed information technology once more in August 2017 (for sitemap priority tag). Changefreq is ignored past the most search engines. Except for Bing, the priority tag still can be used.
Sitemap guidelines
When you will exist creating a sitemap, yous accept to fulfill some limits and follow these rules: Utilize right encoding, character escaping and URL format.
- Employ UTF-viii encoding
- Employ accented URLs If you have the sitemap placed in http://www.instance.com/sitemap.xml, you can't specify a relative URL like /page1.html. You have to use http://world wide web.example.com/page1.html instead.
- You can shrink the sitemap with the gzip method
- Entity escaping:
| Character | Escape lawmaking | |
|---|---|---|
| Ampersand | & | & |
| Single quote | ' | ' |
| Double quote | " | " |
| Greater than | > | > |
| Less than | < | < |
For instance, the URL http://world wide web.example.com/page1.html&lang=en requires escaping of character (&): http://www.example.com/page1.html&lang=en
- Diacritics and other non-ASCII characters escaping: For example, the URL http://www.example.com/päge1.html requires escaping of graphic symbol (ä): http://www.instance.com/p%C3%A4ge1.html
Sitemaps limitations
Each sitemap should incorporate less than fifty,000 URLs, or the file size should non exceed 50MB uncompressed. All limits:

Which URLs should exist put in a sitemap
The selection of ideal URLs into a sitemap is a very important chore. It's non a good practice to list every URL of a website in a sitemap.
Include web pages you want to rank in Google and want to show to the users — important and quality ones.
Exclude:
- Utility pages, which are very needed and useful to users (review form, accounts, wishlists, etc), just are not meant to be landing pages
- Any redirections (3xx), pages with client (4xx) or server (5xx) error pages
- URLs with parameters or id sessions used
- URLs created by filtering (unnecessary for SEO)
- URLs on other subdomains than sitemap.xml are placed; if you have URLs on other subdomains, you take to place another sitemap there
- Canonicalised pages
- Paginated pages
- Indistinguishable pages
- Pages disallowed past robots.txt
- Pages with noindex
4.2. Image sitemap extension
Yous tin extend the XML sitemap with images. Have a look at a basic sitemap again:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > < url > < loc > http : //www.case.com/page1.html</loc> < / url > < / urlset > |
If you desire to add images in that location, add the XML namespace for the images:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-eight" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://world wide web.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.nine" xmlns : prototype = "http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-image/1.i" > < url > < loc > http : //www.example.com/page1.html</loc> < / url > < / urlset > |
Then, add together images in the <url> and image sitemap volition be washed:
| <? xml version = "i.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : image = "http://world wide web.google.com/schemas/sitemap-image/1.1" > < url > < loc > http : //www.example.com/page1.html</loc> < prototype : image > < image : loc > http : //case.com/photograph.jpg</prototype:loc> < / image : epitome > < epitome : image > < paradigm : loc > http : //example.com/image.jpg</epitome:loc> < / prototype : image > < / url > < / urlset > |
<image:paradigm> and <paradigm:loc> tags are required.
Provide more information virtually the images
To fulfill all image sitemap best practices, you can add together more info about each of them:
| Proper name | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Title | <prototype:championship> | The title of the image. You can use the aforementioned text like in the alt attribute of the <img> tag. |
| License URL | <image:license> | A URL to the license of the image, for instance, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/. Cull the right license type or get the link to your license at https://creativecommons.org/choose/. |
| Geographic location | <image:geo_location> | The geographic location of the paradigm, for case, "Berlin, Germany" |
| Caption | <image:caption> | Longer clarification of the image |
A complete case with optional tags:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : image = "http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-paradigm/one.1" > < url > < loc > http : //world wide web.example.com/page1.html</loc> < epitome : image > < image : loc > http : //example.com/photo.jpg</image:loc> < image : title > Grayness cat on the table < / image : title > < image : license > https : //creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/</image:license> < image : geo_location > Berlin , Germany < / paradigm : geo_location > < epitome : caption > Funny cat on the table is looking at photographer . < / epitome : explanation > < / paradigm : image > < / url > < / urlset > |
Epitome sitemap guidelines
- You tin add upwards to 1,000 images for each spider web folio.
- Images don't have to be in the same domain as your website. Yous can use a CDN (content delivery network). Brand sure that your CDN is verified in the Search Console.
4.iii. Video sitemap extension
Provide the required information nigh the videos
You have to add together all of this info about each of them:
| Proper name | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Thumbnail image file | <video:thumbnail_loc> | A URL pointing to the video thumbnail prototype file. Images must be at least 160×90 pixels, and at most 1920×1080 pixels. |
| Title | <video:title> | The championship of the video. You can use the same text like in the alt aspect of <video> tag. |
| Description | <video:description> | Video description must lucifer the description displayed on the web page. |
| Location | <video:content_loc> or <video:player_loc> | At least one of these must exist specified: content_loc points to an URL with bodily video media file; flash is allowed, but may exist indexed less well; player_loc points to a URL with a video actor. Commonly this is the information in the src element of an <embed> tag. |
Don't forget to add the XML namespace for video and utilize <video:video> tag for each URL.
| <? xml version = "i.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : video = "http://world wide web.google.com/schemas/sitemap-video/one.1" > < url > < loc > http : //instance.com/video-page.html</loc> < video : video > < video : thumbnail_loc > http : //case.com/thumb1.jpg < / video : thumbnail_loc > < video : championship > Clown in the garden < / video : title > < video : description > Crazy clown is riding a rabbit . < / video : description > < video : content_loc > http : //world wide web.example.com/video1.mp4</video:content_loc> < / video : video > < / url > < / urlset > |
Provide additional information about the videos
Search engines may use more data well-nigh the videos. Y'all can add together more optional tags:
| Proper name | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | <video:elapsing> | The elapsing of the video in seconds — the max value is 28,800 (8 hours) |
| Expiration date | <video:expiration_date> | Applicable only for videos with the date after which the video will no longer be available, in W3C format |
| Publication date | <video:publication_date> | The date the video was published, in W3C format |
| Rating | <video:rating> | The rating of the video, numbers in the range 0.0 to 5.0 |
| View count | <video:view_count> | The number of times the video has been viewed |
| Family friendly | <video:family_friendly> | Define "no" only if the video should be available but to users with SafeSearch turned off |
| Restriction | <video:restriction> | List of countries where the video may or may non exist played, in ISO 3166 format; requires attribute human relationship with value "let" or "deny" |
| Requiring subscription | <video:requires_subscription> | "Yes" or "no," depending on whether a subscription is required to view the video |
| Live video | <video:live> | "Yes" or "no," depending on whether the video is a live stream |
The complete video sitemap template with optional tags:
| i 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 nine 10 11 12 xiii 14 15 xvi 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.ix" xmlns : video = "http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-video/1.1" > < url > < loc > http : //example.com/video-page.html</loc> < video : video > < video : thumbnail_loc > http : //example.com/thumb1.jpg < / video : thumbnail_loc > < video : title > A clown in the garden < / video : championship > < video : description > Crazy clown is riding a rabbit . < / video : description > < video : content_loc > http : //world wide web.case.com/video1.mp4</video:content_loc> < video : player_loc autoplay = "ap=1" > http : //www.example.com/videoplayer.mp4?video=123</video:player_loc> < video : duration > 600 < / video : duration > < video : expiration_date > 2018 - xi - 05T15 : 20 : 30 + 08 : 00 < / video : expiration_date > < video : rating > three.7 < / video : rating > < video : view_count > 54321 < / video : view_count > < video : publication_date > 2017 - 11 - 05T15 : 20 : 30 + 08 : 00 < / video : publication_date > < video : family_friendly > aye < / video : family_friendly > < video : brake relationship = "deny" > GB USCA < / video : restriction > < video : requires_subscription > no < / video : requires_subscription > < video : live > no < / video : live > < / video : video > < / url > < / urlset > |
Every bit another example, check a video sitemap of The Guardian.
4.4. Alternate languages extension
If your site is written in more languages, you should link them by using "hreflang" attribute so that the search engine gets to know about them hands, understanding which site to show in the search results of specific regions. It'southward the same for sitemaps. By inserting the alternate element to a sitemap, you support the indexation of different language versions.
Every bit a good case of sitemaps with alternate languages extension, this is a sitemap index of Nike with a list of sitemaps for each linguistic communication version.
You must create a separate URL chemical element for each URL. Each URL chemical element must include a <loc> tag indicating the folio URLs, and a <xhtml:link> subelement for every alternate version of the page, including itself.
The <xhtml:link> tag includes attributes to serve the correct language or regional URL: rel="alternate" hreflang="en-usa" href="http://world wide web.example.com/".
Don't forget to add the XML namespace for XHTML.
| ane 2 three iv 5 half dozen 7 viii 9 ten eleven 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <? xml version = "i.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://world wide web.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.ix" xmlns : xhtml = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" > < url > < loc > http : //www.case.com/</loc> < xhtml : link rel = "alternate" hreflang = "en-u.s.a." href = "http://www.example.com/" / > < xhtml : link rel = "alternating" hreflang = "de" href = "http://www.example.de" / > < xhtml : link rel = "alternating" hreflang = "en-gb" href = "http://www.example.co.great britain/" / > < / url > < / urlset > |
4.five. Mobile sitemap extension
A mobile sitemap is useful only for the mobile version sites. If your site uses responsive design to serve mobile users, in that location is no need to create a mobile sitemap, considering the URL is notwithstanding the same. When you comment a mobile version in HTML, mobile sitemap extension is not necessary.
When building the mobile sitemap, add the XML namespace for mobile, and employ<xhtml:link> tag, including attributes to serve the mobile version of the URL: rel="alternate" media="only screen and (max-width: 640px)" href="http://world wide web.k.example.com/".
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : mobile = "http://world wide web.google.com/schemas/sitemap-mobile/1.0" > < url > < loc > http : //world wide web.instance.com/</loc> < xhtml : link rel = "alternate" media = "simply screen and (max-width: 640px)" href = "http://m.example.com/" / > < / url > < / urlset > |
iv.vi. Google News Sitemap
If you have a news site, build a Google News Sitemap. Information technology lets you control which content you submit to Google News. For example, The Guardian has a very well-written news sitemap.
Before you first to use a news sitemap, register your site in Google News, so that Google will be alerted to it. Subsequently the registration, add all of the news articles created in the terminal two days to information technology, with a limit of ane,000 URLs. An update of the sitemap should exist washed each time a news article is published.
Provide information about news articles
You should add this info for each of the following:
| Proper noun | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Publication | <publication> with subtags <news:name> <news:language> | First, include the name of the news publication, and and so the language of your publication. Use an ISO 639 Language Code. |
| Appointment of publication | <publication_date> | Commodity publication engagement in W3C format |
| Title of article | <title> | The title of the news article defined in <h1> heading |
| Keywords | <news:keywords> | Keywords describing the article topic, divided past commas |
| Gengre | <news:genres> | Use <news:genres>Opinion </news:genres> tag, if the article contains just opinions or comments. |
When coding the news sitemap, add the XML namespace for news and employ <news:news> tag for each URL.
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.ix" xmlns : news = "http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-news/0.9" > < url > < loc > http : //www.exampletimes.com/business/articlel55.html</loc> < news : news > < news : publication > < news : name > The Example Times < / news : proper name > < news : language > en < / news : language > < / news : publication > < news : publication_date > 2017 - ten - 20T17 : 30 : 00 - 02 : 00 < / news : publication_date > < news : keywords > Business , Sells , Retail < / news : keywords > < news : championship > Consumers announced loth to spend < / news : championship > < / news : news > < / url > < / urlset > |
For better displaying your article in Google News, try to add <image:image> tag, along with the location of a representative image. Commonly, Google picks the epitome from the article, but without defining the image in a sitemap, your article can be displayed in Google without it.
The consummate Google News sitemap example:
| i ii 3 iv 5 6 7 8 nine 10 11 12 13 14 15 xvi 17 18 | <? xml version = "i.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://world wide web.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : news = "http://world wide web.google.com/schemas/sitemap-news/0.9" > < url > < loc > http : //www.exampletimes.com/business organization/articlel55.html</loc> < news : news > < news : publication > < news : name > The Example Times < / news : name > < news : language > en < / news : linguistic communication > < / news : publication > < news : publication_date > 2017 - 10 - 20T17 : 30 : 00 - 02 : 00 < / news : publication_date > < news : championship > Consumers appear loth to spend < / news : title > < / news : news > < image : image > < image : loc > http : //instance.com/photo.jpg</image:loc> < / paradigm : image > < / url > < / urlset > |
A big plus is that readers of RSS feed can add together Google News sections to their RSS aggregators. Your articles will be shown in Google News and and so will in RSS feed.
An RSS feed is a small file containing the most ten recent fresh updates to your website.
Provide the required information well-nigh the URLs
You have to add all of this information for the channel in the <channel> tag and for each URL in the <particular> tag:
| Proper name | Tag | Clarification |
|---|---|---|
| Championship | <title> | The championship of an article defined in the <h1> heading |
| Link URL | <link> | Link pointing to an article destination |
| Description | <clarification> | Description of an article |
| <? xml version = "i.0" encoding = "UTF-eight" ?> < rss version = "2.0" > < channel > < title > The example web log < / title > < link > https : //world wide web.exampleblog.com/feed</link> < description > On - page and technical SEO tips < / clarification > < item > < title > Sitepams < / championship > < link > https : //www.exampleblog.com/article-near-sitemaps/</link> < description > This commodity is about sitemaps . < / description > < pubDate > Mon , 30 Oct 2017 14 : 00 : 52 + 0000 < / pubDate > < / particular > < / channel > < / rss > |
Provide more than data about the URLs
Even if these tags are non important for SEO and site indexation, they are important to your readers. The more than information yous provide, the more data RSS feed readers will become about your posts in their RSS aggregators.
| Proper name | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Language | <language> | Language availability — RSS aggregators will group sites based on their language |
| Image of web log | <image> | Prototype link points to an image/logo destination |
| Description | <description> | Text clarification of an article. |
| Publication appointment | <pubDate> | Engagement and time of publication in RFC 822 date-fourth dimension format |
| File enclosure | <enclosure> | A media-file included with an item |
| Category | <category> | Category division — RSS aggregators will grouping sites based on category. If ii or more than categories are applicative, apply the <category> tag separately for each category. |
The RSS sitemap template with optional tags:
| one 2 3 iv v 6 7 8 9 10 eleven 12 13 xiv fifteen 16 17 18 xix 20 21 | < rss xmlns : media ="http : //search.yahoo.com/mrss/"version="2.0"> < channel > < title > Spotibo < / title > < link > https : //weblog.spotibo.com/feed</link> < description > On - page and technical SEO tips < / clarification > < language > en - gb < / linguistic communication > < image > < url > https : //weblog.spotibo.com/images/logo.png</url> < championship > Spotibo < / title > < link > https : //weblog.spotibo.com/</link> < / paradigm > < item > < title > Sitemaps < / title > < link > https : //blog.spotibo.com/article-about-sitemaps </link> < description > This commodity is about sitemaps . < / description > < enclosure url = "https://blog.spotibo.com/sitemap-tutorial.mp3" length = "5000" blazon = "audio/mpeg" / > < category > SEO < / category > < / item > < / channel > < / rss > |
If you run a web log on WordPress, an RSS feed is generated automatically and updated at the URL www.instance.com/feed/.
The concluding step is submitting your feed to an aggregator that will friction match the interest. At that place are many popular aggregators where you should try to submit your website.
mRSS feed is the same as an RSS sitemap, but with only one difference — information technology's made for video content. A prissy example is Vimeo mRSS feed.
| Name | Tag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Media content | <media:content> | Parent of all the media tags |
| Media role player | <media:role player> | Link pointing to a video actor |
| Media credit | <media:credit> | Requires aspect function and scheme linking to an author bio |
| Media thumbnail | <media:thumbnail> | A thumbnail with a link to its destination |
| Media title | <media:title> | A championship of a video — can be the same as an item championship |
| 1 ii 3 4 5 half-dozen vii viii nine 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 xix | < rss xmlns : media = "http://search.yahoo.com/mrss/" version = "2.0" > < channel > < championship > Spotibo < / title > < link > https : //blog.spotibo.com/feed</link> < description > On - page and technical SEO tips < / description > < item > < championship > Sitemaps < / championship > < link > https : //www.exampleblog.com/article-about-sitemaps </link> < clarification > This article is near sitemaps . < / description > < pubDate > Mon , 30 October 2017 14 : 00 : 52 + 0000 < / pubDate > < media : content > < media : player url = "https://www.case.com/video/1234" / > < media : credit role = "author" scheme = "https://www.example.com/user12" > < / media : credit > < media : thumbnail peak = "540" width = "960" url = "https://www.example.com/video/1234.webp" / > < media : title > Sitemaps < / media : championship > < / media : content > < / item > < / channel > < / rss > |
Create a construction for sitemaps with a sitemap alphabetize
When you will create well-structured sitemaps, it greatly helps you lot with monitoring of indexation.
Search Console provides information nigh how many URLs in each sitemap are indexed. Have a wait at this sitemap dashboard:
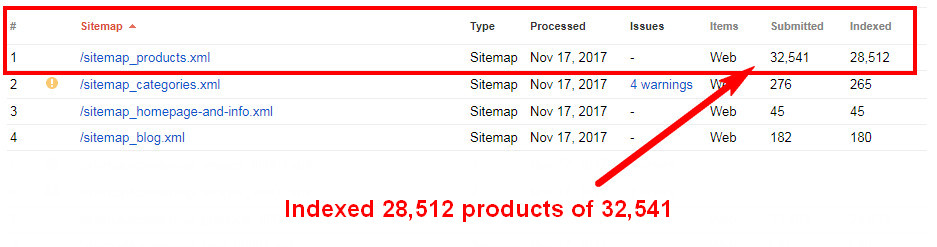
It's much easier to examine indexation issues for separate sitemaps than just for one large file.
You tin connect more than sitemaps together with a sitemap index. In the example of the CNN website's sitemap index, they build 3 sitemaps differing past content every month and then update them in the sitemap index file.
Implementation of a sitemap index
Here is the template of the sitemap index with two files:
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < sitemapindex xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > < sitemap > < loc > http : //www.case.com/sitemap1.xml</loc> < lastmod > 2017 - xi - 05T12 : 00 : 00 - 02 : 00 < / lastmod > < / sitemap > < sitemap > < loc > http : //world wide web.case.com/sitemap2.xml</loc> < lastmod > 2017 - xi - 05 < / lastmod > < / sitemap > < / sitemapindex > |
Only <loc> tag is required. Only I recommend add <lastmod> too. You tin notice how to format date & time above. To a sitemap index, you can add together upward to l,000 sitemaps. And to Search Console, you can add 500 sitemap indices.
Validate your sitemaps
Generated sitemaps can be much too complex, and information technology is easy to brand a mistake. After you generate a sitemap, I would recommend validating it with Yandex Sitemap Validator and after that with Google Search Panel.
Yandex Sitemap Validator
Yandex's validator is very easy to use. Yous tin can input text, a URL with a sitemap or merely upload a file.
What validator checks:
- Checks basic XML sitemaps, RSS feeds and Sitemap Indexes. Unfortunately, information technology doesn't help you lot with sitemap extensions similar Image sitemaps.
- Checks XML syntax
- Shows file sizes
- Shows the number of links in the sitemap
Yandex Sitemap Checker serves the results immediately. It is a cracking tool for initial sitemap testing or for checking the sitemaps of domains which yous don't own.
Google Search Panel
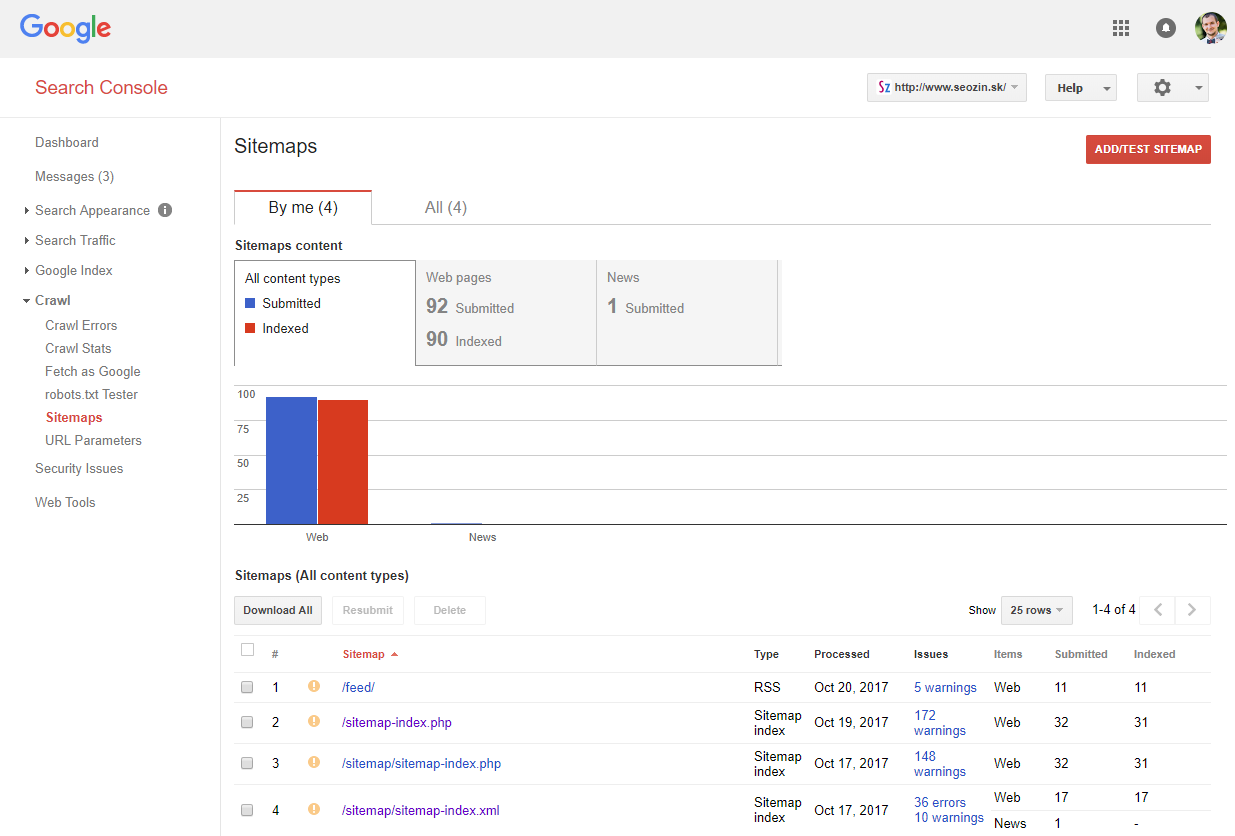
The search console checks nearly everything, including all sitemap extensions, URL status codes and much more.
It is the all-time solution for your sitemap testing. It takes the Search Console some time to go on them, though — from hours to a few days. And yous can't test a text input or sitemaps on external domains.
v. Notify the search engines about a sitemap
In order for search engines to process the sitemap, they must commencement learn about them, otherwise, the sitemaps are useless for SEO. There are several ways of doing this:
Methods the search engines utilise to notice and use your sitemap
Yous tin combine more than one of the following methods:
- Put the sitemap location at robots.txt.
- Write the sitemap location in the source code.
- Submit the sitemap via the search engine'due south webmaster tools.
- Register yourself equally a publisher to use Google News Sitemap.
Robots.txt
The safest style to get to know nearly your sitemap is to update the XML sitemap in the robots.txt file. Every search engine will find it in in that location.
You tin define more than one sitemap, and its URL must exist absolute.
Definition of XML sitemap in robots.txt:
| Sitemap : http : //www.case.com/sitemap-path1.xml Sitemap : http : //world wide web.example.com/sitemap-path2.xml Sitemap : http : //world wide web.example.com/sitemap-path3.xml |
The biggest issue here is that y'all make your sitemaps public so that anyone can easily find them. However, you lot should remember most that, because in the worst scenario, it can exist abused by your competition.
Source code
RSS feed is a fiddling fleck different and has to be added to the source code.
| < link rel = "alternate" type = "application/rss+xml" href = "rss-path" > |
The search engines tin can likewise learn nigh your sitemap from the unproblematic <a> tag linking to the sitemap destination, simply this method is not reliable, and in that location's no guarantee that every engine will notice it.
Search engine'south webmaster tools
Non all search engines have their ain webmaster tools. If an XML sitemap does not need to be confidential, it should also be listed in robots.txt.
Google Search Panel
- Open the Search Console and click on "Sitemaps" under "Clamber."
- Click on "Add/Test Sitemap" and paste your XML Sitemap file here and click "Test" button before hitting the "Submit" button.
- After this pace, yous can see how many spider web pages and other files were institute in the sitemap; click "Close exam" and hitting "Submit."
- Now repeat the process and copy all of the sitemaps yous have one-by-1 in the webmaster tools. If the sitemaps are listed in a sitemap index, you need to submit the index merely.

You can submit up to 500 sitemaps index files in Search Panel.
Bing Webmaster Tools
- Open Bing Webmaster Tools.
- At present click on Dashboard- > Configure my site -> Sitemap.
- Copy and paste the XML sitemap in the Bing sitemap box, so striking the "Submit" button.
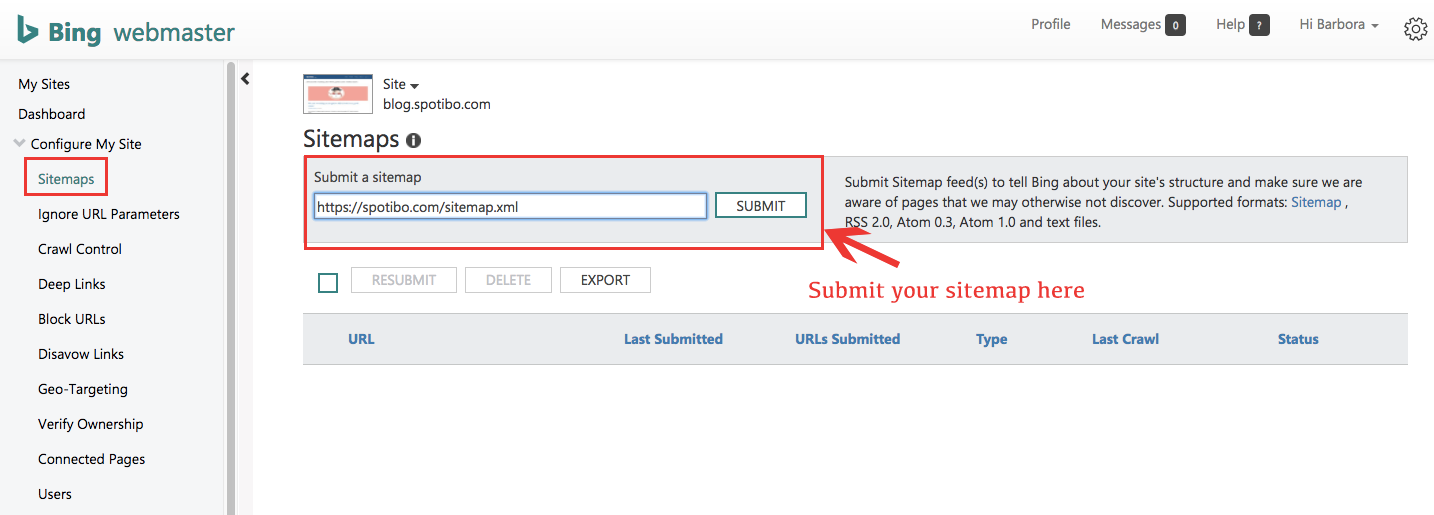
With Bing Webmaster Tools, you can only see the number of submitted pages, simply non those that are indexed. Therefore, analysing data is not as like shooting fish in a barrel as in Search Console. The same is truthful for Yandex.
Yandex Webmaster Tools
- Open Yandex Webmaster Tools.
- Click on Dashboard -> Indexing -> Sitemaps file.
- Re-create and paste the XML sitemap in the Yandex sitemap box and striking the "Add" button.
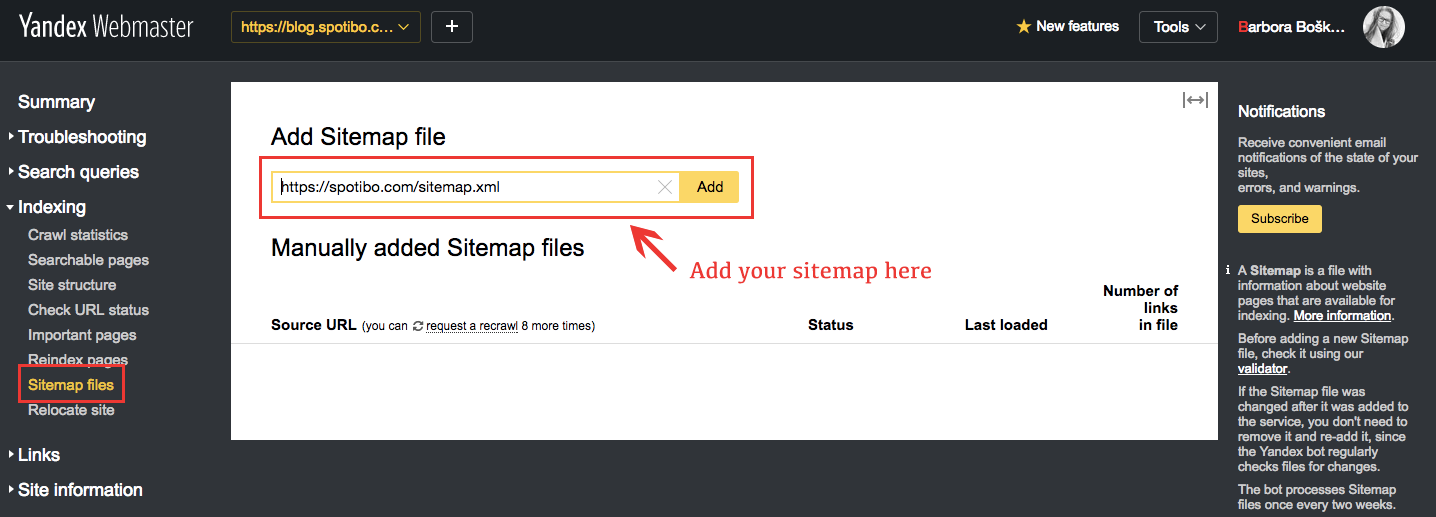
Register yourself as a publisher to use News Sitemap
Until your site is included in Google News, Google doesn't employ your news sitemap. You can request inclusion in the Google News Publisher Eye:
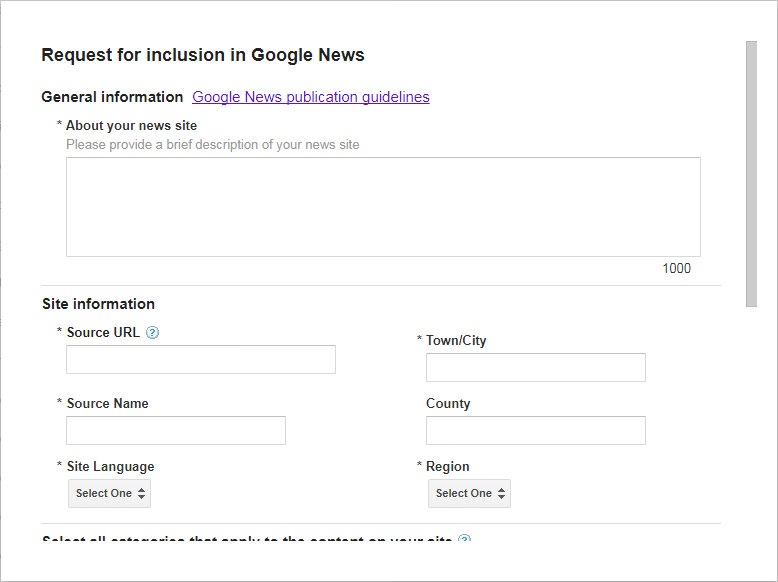
Earlier your request, read this pace-past-step guide from Shane Barker and the official Google guidelines.
Your competitors can abuse a visible sitemap
Location of a sitemap in robots.txt or the source code is public. Anyone can find it. If y'all have a well-structured and complex sitemap, competitors can easily get abusable data, like the listing of categories, tags or all your products.
On the other mitt, even if you lot don't have visible sitemap and competitors want that information, they volition get information technology. But they'll have to try harder. To obtain and clean the information, they take to use a web crawler. But this way is much harder than to simply parse sitemap files.
Just be conscientious. If you become 99% of your traffic from Google, Bing and other search engines which accept their own webmaster tools, consider the privacy of your sitemaps. Information technology is non necessary to link to your sitemap in the robots.txt file.
Ping search engines immediately after every update
When adding a new site to a sitemap, y'all can warning the search engines through so-called "pinging." They volition know nigh the changes immediately, and they can so index the new content.
"Ping" your sitemap in the search engine by entering a customized URL:
- Google: http://world wide web.google.sk/ping?sitemap=http://example.com/sitemap-path.xml
- Bing: http://world wide web.bing.com/ping?sitemap=http://instance.com/sitemap-path.xml
For any other search engine, endeavor to utilize this URL template:
| < searchengine_URL > / ping ? sitemap = http : //example.com/sitemap-path.xml |
Although not every search engine supports it, it is ideal if you can automate "pinging". Whenever you update a sitemap on the server, send a notification to Google or Bing as well.
Get the free sitemap cheatsheet
Get your overview of all important information in one piece:

Summary
Sitemaps aid yous with faster and better indexation, along with the monitoring of indexed pages. They are most suitable for websites with thousands of pages and for frequently updated content. When y'all desire to implement sitemaps, y'all accept to go through three steps:
- Choose the right types of sitemaps
- How to implement them
- Notify search engines nigh sitemaps
You should follow sitemap guidelines, limitations and avert the static sitemap generators. And then you will benefit from all of the advantages of sitemaps.
Are you proud of your sitemaps structure? Let us know in the comments or via janko@spotibo.com. We would like to link to some well-built sitemaps. 🙂
FAQ
I have got a lot of questions about this topic and this article became really looong. When you don't want to read it all, here are direct answers to the well-nigh frequently questions:
What is a sitemap for, are sitemaps important for SEO?
Sitemaps don't assist you with amend search rankings. It is not a ranking gene. Only it is often important for SEO. Benefits of sitemaps are:
- Faster indexation
- Better indexation of deep pages
- Monitoring of indexed pages
Read more about the purposes of sitemaps to a higher place.
How many types of sitemaps are there in SEO?
There are ii of import kinds of sitemaps: XML and RSS sitemap. XML sitemap has v extensions for images, videos, mobile, alternate language, and news. RSS sitemap can be extended with mRSS.

How to discover my sitemap URL?
- Check an URL www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml.
- Cheque the sitemap location at www.yourdomain.com/robots.txt.
- Check the sitemap location in the source code.
- Bank check the sitemap via the search engine'south webmaster tools similar Google Search Panel.
More details on how to find your sitemap, yous will notice above.
How to use XML sitemap?
You can employ sitemaps to:
- Monitoring of indexed pages: In combination with Google Search Panel, it is possible to find out which URLs are covered in the sitemap that Google indexes.
- Faster indexation: Search engine will detect out almost new pages faster, therefore, the indexation process and displaying the website in search results volition be faster as well.
- Better indexation of deep pages: Search engines can find out the pages that were not discovered while crawling the website. Just it doesn't necessarily hateful that all of them will be indexed.
How many sitemaps should I have?
A sitemap isn't necessary for every website. Simply when y'all demand it, each should contain less than50,000 URLs, or the file sizeshould not exceed 50MB. So if your site has 100,000 URLs, y'all volition need ii sitemap files at least. For bigger sites is a good practice to carve up XML sitemaps past webpage types like products, categories, articles, etc.
How to create a sitemap for Google?
Google support all common sitemap types. You tin generate XML or RSS file types. Examples and templates of sitemaps for Google are described above.
How to add a sitemap to google?
- Open the Search Console and click on "Sitemaps" under "Clamber."
- Click on "Add/Exam Sitemap" and paste your XML Sitemap file here and click "Exam" push before hitting the "Submit" button.
- After this step, you can see how many web pages and other files were found in the sitemap; click "Close examination" and striking "Submit."
- Now repeat the process and re-create all of the sitemaps you lot take one-by-one in the webmaster tools. If the sitemaps are listed in a sitemap index, you need to submit the index merely.
Proficient sitemap example and templates
XML sitemap example
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-viii" ?> <urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" > <url> <loc> http://www.case.com/page1.html </loc> <lastmod> 2017-10-20T17:xxx:00-02:00 </lastmod> </url> </urlset> |
Bound to XML sitemap guidelines and more than templates.
Image sitemap case
| <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-eight" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : image = "http://world wide web.google.com/schemas/sitemap-image/i.1" > < url > < loc > http : //www.case.com/page1.html</loc> < image : image > < paradigm : loc > http : //case.com/photo.jpg</image:loc> < image : title > Grayness cat on the table < / paradigm : title > < epitome : license > https : //creativecommons.org/licenses/past-sa/2.0/</image:license> < image : geo_location > Berlin , Germany < / prototype : geo_location > < image : caption > Funny true cat on the table is looking at photographer . < / image : explanation > < / image : image > < / url > < / urlset > |
Spring to prototype sitemap guidelines and more templates.
Video sitemap example
| 1 two three 4 5 6 7 8 9 x 11 12 13 fourteen fifteen xvi 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | <? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : video = "http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-video/1.1" > < url > < loc > http : //example.com/video-folio.html</loc> < video : video > < video : thumbnail_loc > http : //example.com/thumb1.jpg < / video : thumbnail_loc > < video : title > A clown in the garden < / video : title > < video : description > Crazy clown is riding a rabbit . < / video : description > < video : content_loc > http : //www.example.com/video1.mp4</video:content_loc> < video : player_loc autoplay = "ap=1" > http : //www.instance.com/videoplayer.mp4?video=123</video:player_loc> < video : duration > 600 < / video : duration > < video : expiration_date > 2018 - 11 - 05T15 : 20 : xxx + 08 : 00 < / video : expiration_date > < video : rating > iii.vii < / video : rating > < video : view_count > 54321 < / video : view_count > < video : publication_date > 2017 - xi - 05T15 : 20 : 30 + 08 : 00 < / video : publication_date > < video : family_friendly > aye < / video : family_friendly > < video : restriction relationship = "deny" > GB USCA < / video : restriction > < video : requires_subscription > no < / video : requires_subscription > < video : live > no < / video : live > < / video : video > < / url > < / urlset > |
Spring to video sitemap guidelines and more templates.
Hreflang sitemap example
| i ii 3 4 5 half dozen vii 8 9 10 xi 12 13 14 fifteen 16 17 18 xix | <? xml version = "one.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < urlset xmlns = "http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns : xhtml = "http://world wide web.w3.org/1999/xhtml" > < url > < loc > http : //www.example.com/</loc> < xhtml : link rel = "alternate" hreflang = "en-u.s.a." href = "http://www.case.com/" / > < xhtml : link rel = "alternate" hreflang = "de" href = "http://www.case.de" / > < xhtml : link rel = "alternate" hreflang = "en-gb" href = "http://world wide web.instance.co.united kingdom of great britain and northern ireland/" / > < / url > < / urlset > |
Jump to alternate language sitemap guidelines and more than templates.
| ane 2 iii 4 5 six 7 8 ix 10 xi 12 xiii 14 15 sixteen 17 18 19 20 21 | < rss xmlns : media ="http : //search.yahoo.com/mrss/"version="2.0"> < channel > < title > Spotibo < / title > < link > https : //blog.spotibo.com/feed</link> < description > On - page and technical SEO tips < / description > < language > en - gb < / linguistic communication > < prototype > < url > https : //web log.spotibo.com/images/logo.png</url> < championship > Spotibo < / championship > < link > https : //web log.spotibo.com/</link> < / paradigm > < item > < title > Sitemaps < / title > < link > https : //weblog.spotibo.com/article-about-sitemaps </link> < description > This article is about sitemaps . < / clarification > < enclosure url = "https://web log.spotibo.com/sitemap-tutorial.mp3" length = "5000" type = "sound/mpeg" / > < category > SEO < / category > < / detail > < / channel > < / rss > |
Bound to RSS guidelines and more templates.
Source: https://blog.spotibo.com/sitemap-guide/
0 Response to "How to Upload an Image Sitemap to Google"
Post a Comment